What is fluorescence?
Fluorescence is the energy that the electrons in the material absorbs from the low energy state to the high energy state, and then returns to the low energy state, which is the non-temperature radiation light-cold light. That is: the material absorbs short-wave light, enters the excited state, and emits long-wave light.
Whether it is autofluorescence of a substance, a fluorescent dye or a fluorescent protein expressed by fusion, it is required to undergo a specific wavelength of light excitation (excitation), and after electron migration, after a loss of energy, a specific long-wavelength light (emitation light Emision) is emitted. It can be collected by the detection system to achieve the function of identifying specific fluorescence.
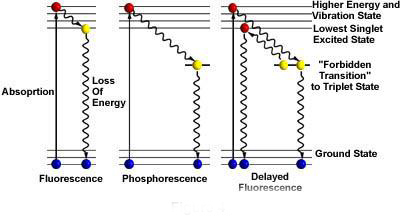
What is the fluorescent light cube?
In fluorescence microscopy and imaging, fluorescent light cubes provide specific wavelengths of excitation light and corresponding long-wavelength emission light to collect fluorescent signals through the naked eye, display screen or camera. Therefore, the fluorescent light cube determines what can be detected. The key components of the fluorescent signal, its characteristics include EX: excitation wavelength filter parameters, EM: emission wavelength filter parameters and DM: bisection parameters. Take the DAPI light cube of Revolve's inverted inverted fluorescence microscope as an example, EX: 385/30, EM: 450/50, DM: 425.
The light emitted by the light source passes through DAPI EX to obtain excitation light of a specific wavelength range, that is, light of 385±15 nm is obtained, and the fluorescent substance which can be excited in this range is specifically excited; the DM bipartite mirror separates the excitation light from the fluorescence. Optical components, as special mirrors, reflect only light of a specific wavelength, allowing all other wavelengths to pass, so only light energy > 425 nm is transmitted to the EM; EM emission filters are fluorescent and other backgrounds Optically separated optical components. The emission filter transmits the fluorescent wavelength of light through the dichroic mirror while blocking all other light that leaks from the excitation source (reflected from the sample or optical element). The wavelength of the emitted light is greater than EM to be observed, ie only light in the range of 450 ± 25 nm enters the detection system. Choosing the right EX, EM filter and DM splitter can help researchers achieve a higher signal-to-noise ratio (S / N).
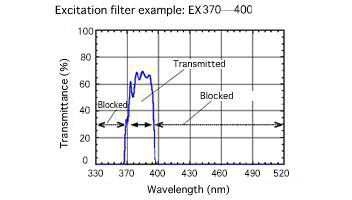
Excitation filter (EX) - Excitation filter works:
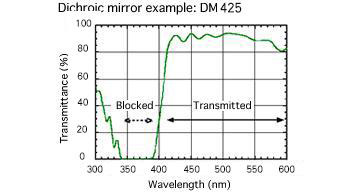
The Dichroic mirror (DM) splitter works:
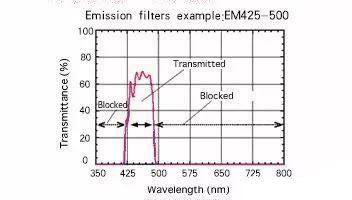
Emission (EM) filters emit filters to work:
Revolve's Inverted One-Phase Fluorescence Microscope offers six light cube options and personalization services, and is fully automated with the iPad Pro and Echo app. The light source is a high-energy LED with long life, low photobleaching, and no mercury contamination risk. The sheets are Chroma® spray-coated filters with ultra-high light transmittance. The optical properties of the six light cubes are as follows:
EX | EM | DM | |
DAPI | 385/30 | 450/50 | 425 |
FITC | 470/40 | 525/50 | 495 |
TRITC | 530/40 | 590/50 | 560 |
TxRed | 560/40 | 635/60 | 600 |
ALEXA 594 | 580/30 | 635/60 | 594 |
Cy5 | 640/30 | 690/50 | 660 |
Revolve provides up to 4 EPI fluorescence channels and 1 transmitted light channel, which can automatically superimpose 5 channels of images, and can still adjust the image of each channel on the superimposed image, which provides great research for scientists. Convenience.
Youth Biotech CO,. Ltd. , https://www.youtherb.com