Documentary notes

Partial loss of psychiatric risk gene Mir137 in mice causes repetitive behavior and impairs sociability and learning via increased Pde10a
Nature Neuroscience IF=19.912
Original link: https://
Research materials and methods
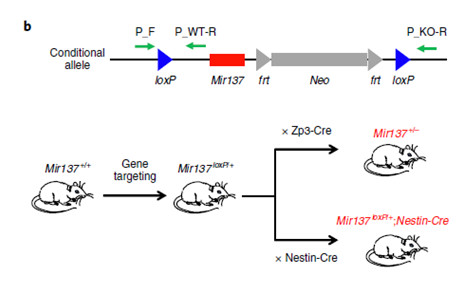
Mir137-knockout mice
(1) Evaluation of the effects of neurological function after miR-137KO:
â— Synaptic plasticity: immunohistochemistry, spinendensities, dendritic length, etc.
â— Learning and memory: Morriswater maze test, Barnes maze test, long-termpotentiation (LTP), etc.
â— Repeated behavior and social skills: marbleburyingtest, social interaction test, the three-chamber test, etc.
(2) Proteome analysis:
â— Technology: TMT quantification
â— Sample: cortical tissue
◠Groups and replicates: Mir137+/+, Mir137+/–, and Mir137–/–, two biological replicates per group (from two litters)
(3) Transcriptome analysis:
Sample with proteome
(4) Combined analysis of transcriptome + proteome to find direct regulation of miR-137:
The Sylamer algorithm compares the correlation between UTR matching enrichment results and protein differential expression, and further compares mRNA differential expression levels.
(5) Verify the direct target of miR-137:
Luciferase reporter assay
Research content and results
1. Analysis of synaptic protein immunohistochemistry and dendritic length revealed that miR-137 KO can cause impaired neuroplasticity.
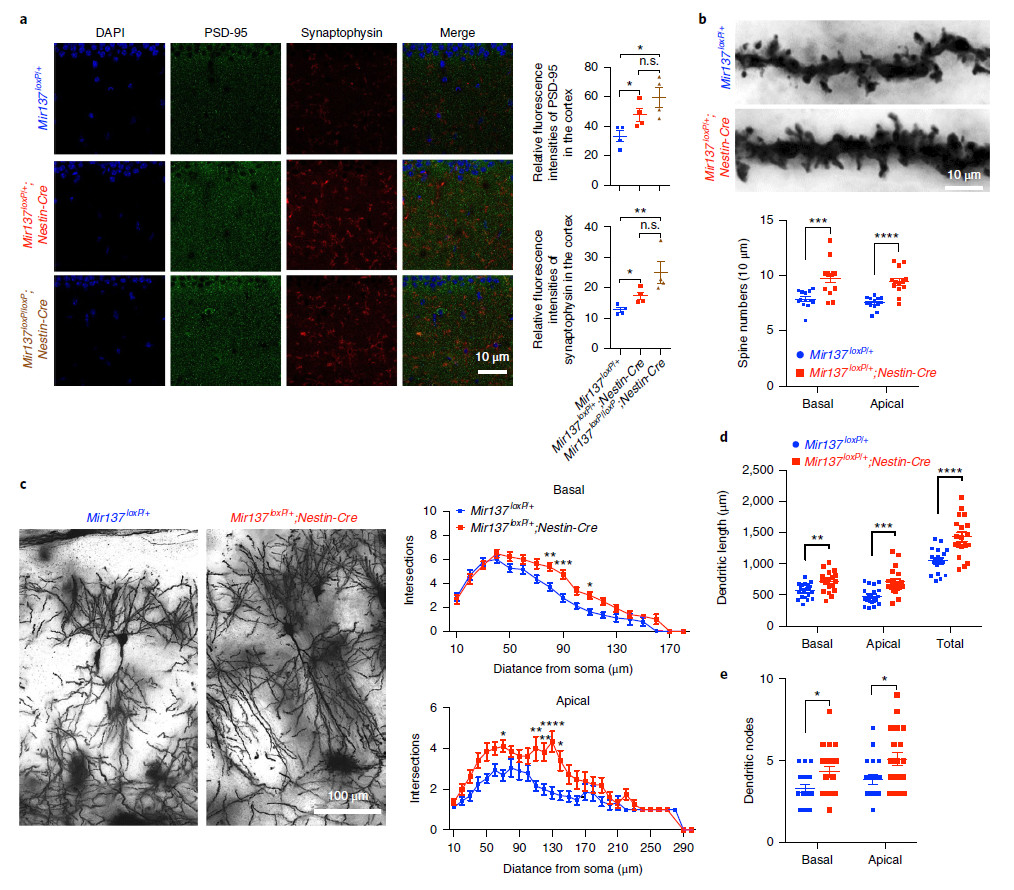
Fig. 2 |Loss of miR-137 in the nervous system leads to synaptic overgrowth and impaireddendritic growth in vivo
2. Multiple behavioral tests revealed that miR-137 KO can cause learning and memory dysfunction.
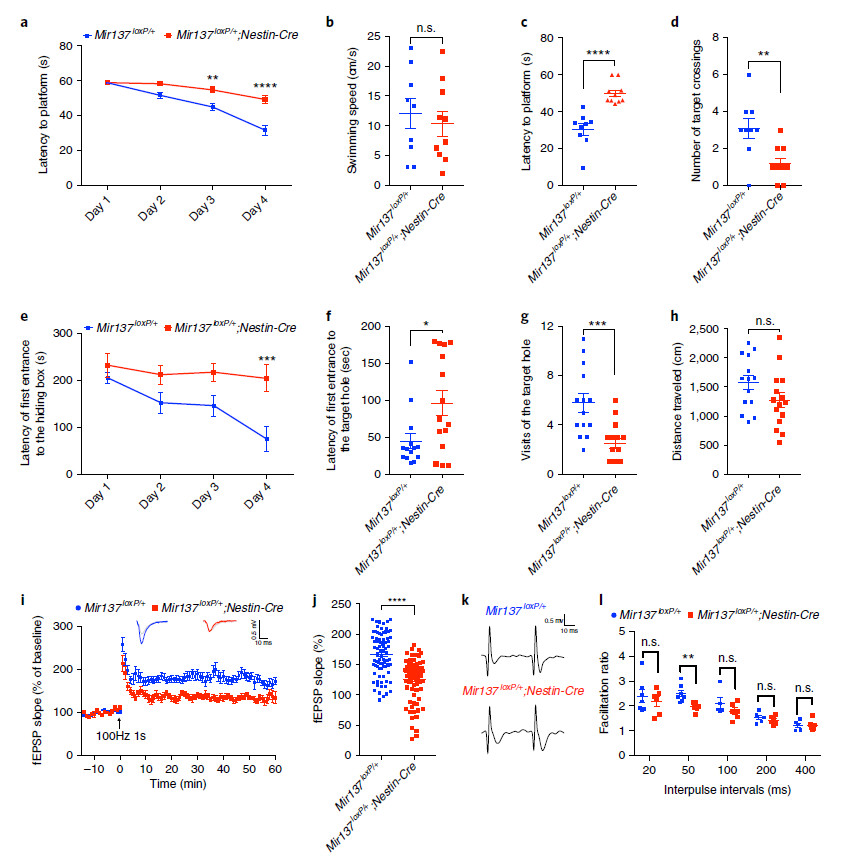
Fig. 3 | Partial loss of miR-137 leads to the learning and memory deficits.
3. A variety of behavioral tests revealed that miR-137 KO can lead to changes in social ability.
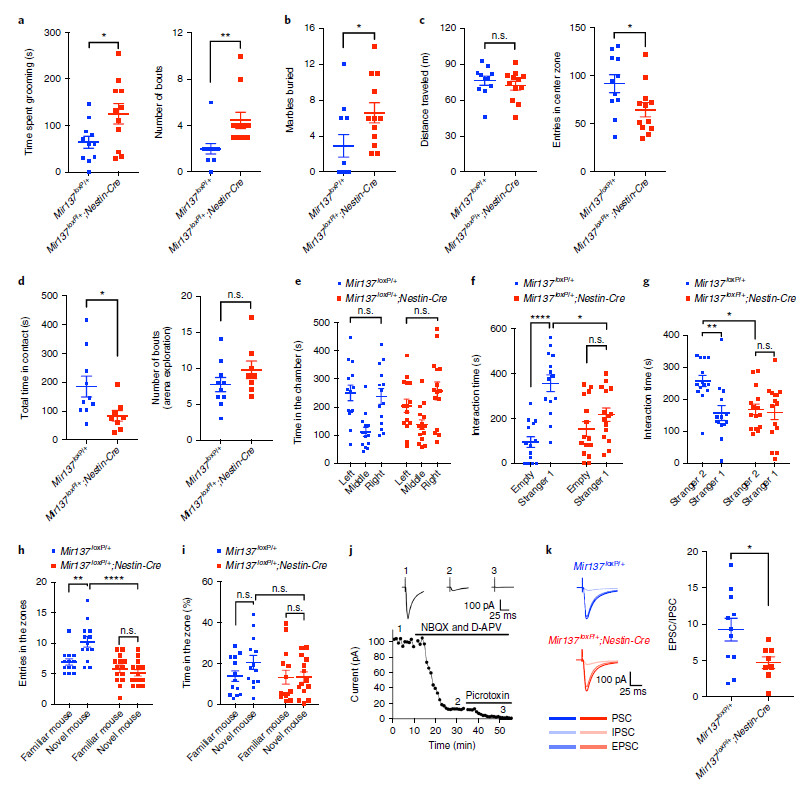
Fig. 4 | Partial loss of miR-137 causes impaired socialbehaviors in mice
4. The transcriptome and proteome revealed miR-137 regulatory substrates.
The proteome results showed that 419, 94 and 76 differentially expressed proteins were screened in the Mir137–/– group, the Vers Mir137+/+ group, the Mir137+/– group, the Vers Mir137+/+ group, and the Mir137–/– group, the Versus Mir137+/– group. . These proteins are involved in biological processes such as DNA replication, nervous system development, and chromatinremodeling, peptidase activity regulation, acute-phaseresponse, and regulation of neurotransmitter secretion. Among them, 41 up-regulated proteins and 9 down-regulated proteins were predicted to be substrates for miR-137. By further comparison with the results of RNAseq, there were 37 genes corresponding to the 41 up-regulated proteins, and there was no significant difference in mRNA expression level, indicating that the above genes may be directly regulated by miR-137 through post-transcriptional regulation. .
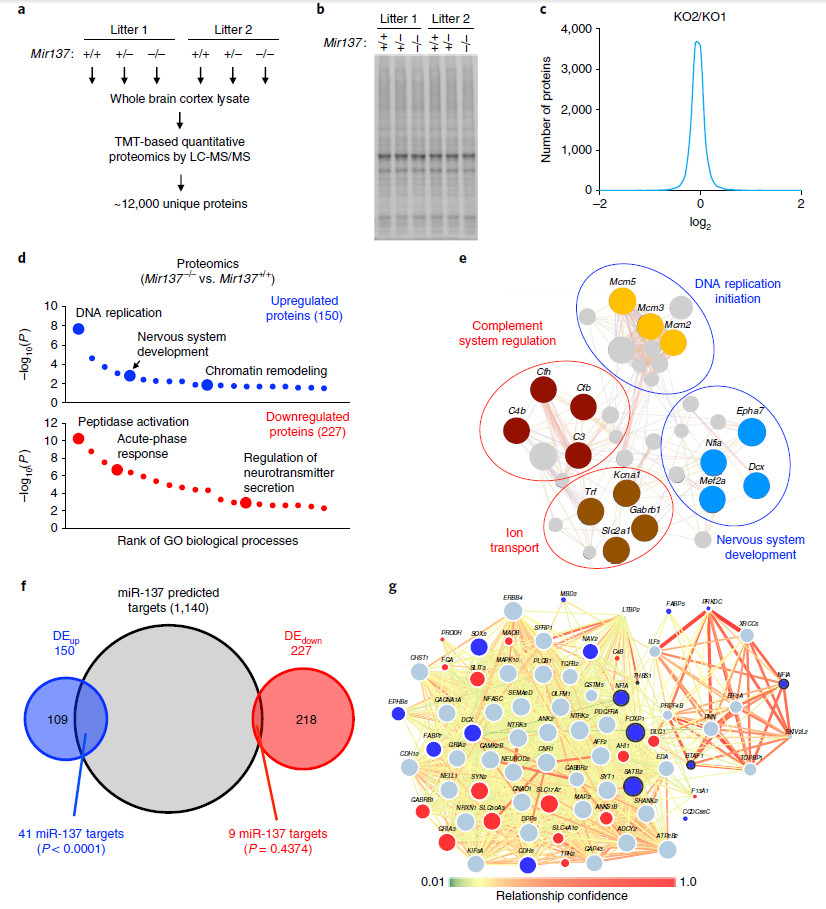
Fig. 5 | Systematic identification of in vivo mRNA targetsof miR-137 by integrating proteomic, transcriptomic, and bioinformaticanalyses.
5. Confirm that Pde10a gene is a direct regulatory substrate for miR-137
Among the above 37 genes, the authors selected five genes corresponding to the most prominent proteins, and five neurologically related genes. The luciferase reporter assay +UTR mutation was used to confirm that the Pde10a gene is a direct regulatory substrate for miR-137.
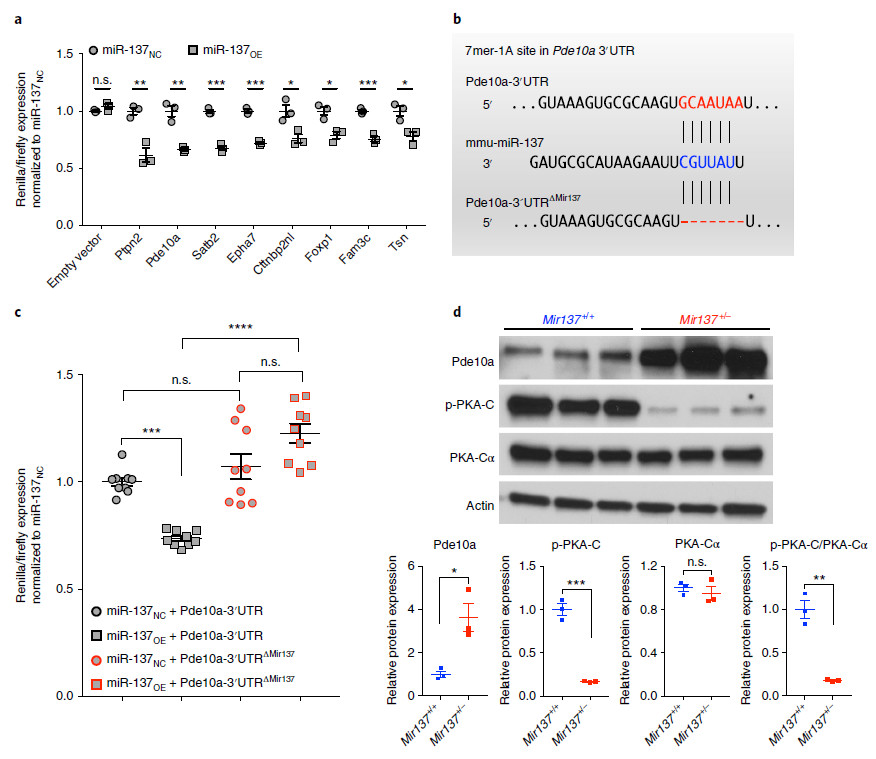
Fig. 6 | Pde10a is akey mRNA target of miR-137.
6. follow up research
Inhibition of Pde10a expression can slow down neurological dysfunction caused by miR-137 KO. Pde10a KO reverses neurological dysfunction caused by miR-137 KO.
Summary and extension
The article has a clear idea: it is possible to develop miRNAs that may play an important role in previous genetic studies. Based on the KO animal model, the biological function of miRNA was first evaluated. Multi-omics data were then used to screen for possible miRNA substrates, followed by classical methods for direct substrate validation; and finally, phenotypic changes after substrate intervention were evaluated. Thereby to achieve the analysis of the target miRNA function and mechanism of action.
Among them, the method of screening miRNA substrates is worth learning . Because there are still many inaccuracies in the conventional prediction of substrates by sequence alignment. The analysis of the proteome can clearly tell us which protein products actually have the corresponding expression changes, and the expression level of the protein products is the most important basis for the determination of miRNA substrates. At the same time, if the mRNA corresponding to the differentially expressed protein does not change accordingly, it can be further determined that the regulation of the gene is not due to changes in the level of transcription of the gene, but rather to the regulation of the post-transcriptional level of miRNA involvement (another way is The binding of miRNAs causes degradation of mRNA). Therefore, based on substrate prediction, the proteome + transcriptome can more accurately and efficiently screen miRNA substrates and provide more comprehensive and systematic information.
Suture Needle,Chromic Catgut Suture,Chromic Suture,Medical Disposable Suture
Surgimed Medical Supplies Co.,Ltd , https://www.surgimedcn.com