According to Wikipedia, as of 2014, there were more than 420 million people with diabetes worldwide. This number has decreased in recent years, but the situation is still not optimistic. As one of the complications of diabetes, Diabetic Retinopathy is eroding long-term diabetic patients. Medical people have found that for the average patient, more than 10 diseases will begin to develop lesions, leading to blindness. It sounds very far after 10 years, but the situation is actually more urgent than imagined, because for those patients with poor glycemic control or insulin-dependent diabetes, they are more likely to have fundus lesions earlier, and the risk of blindness is higher than other People and even people with diabetes are higher.
The problem is particularly serious in South Asian countries. As of 2015, there are more than 70 million people with diabetes in India, and due to social reasons such as lifestyle habits, genetic factors, lack of doctors and adequate medical resources, the situation in the next 20 years is very worrying. By 2040, South Asian countries have diabetes The number will grow to 140 million. But the direct problem facing the Indian public health sector is even more difficult: according to official statistics, because there is a gap of about 120,000 ophthalmologists across the country, there are no doctors for diabetes and diabetic retinopathy, and about 45% are Some or all of my vision has been lost before the diagnosis...
Lily Peng is a researcher at Google Research, a Google research organization. On the eve of the upcoming Google Developers Conference I/O17, she introduced us to an exciting research project: using machine learning techniques to detect diabetic retinopathy early, for timely and even preventive treatment, so that those might People who lose their vision after 3, 5 or even 10 years get a valuable opportunity for early treatment.
"Our mission: Using deep learning techniques to train an algorithm that automatically diagnoses potential lesions from the patient's retinal fundus photos," she said. The task logic sounds simple, but it is not, because the process of training this algorithm is the key. To provide high-quality training materials, the researchers recruited 54 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-qualified ophthalmologists and professionals for a total of 128,175 retinal fundus photographs from May to December 2015. The material is tagged and rated, eventually marking more than 880,000 confirmed symptoms.
Next, neural network technology should come in handy. Lily Peng's team built a 26-layer Convolutional Neural Network and trained it with labeled material.
This kind of neural network structure is special, its characteristic is that it has good performance for the data of two-dimensional structure - that is, picture - so it is often used to learn a large number of pictures.
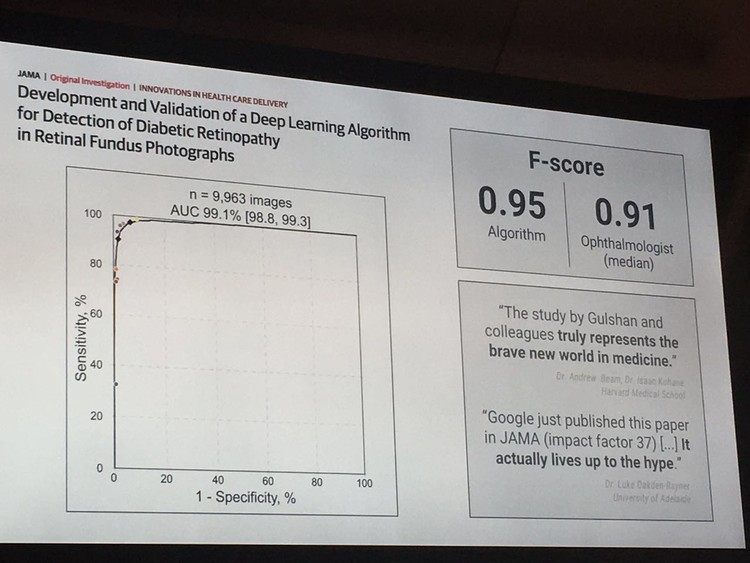
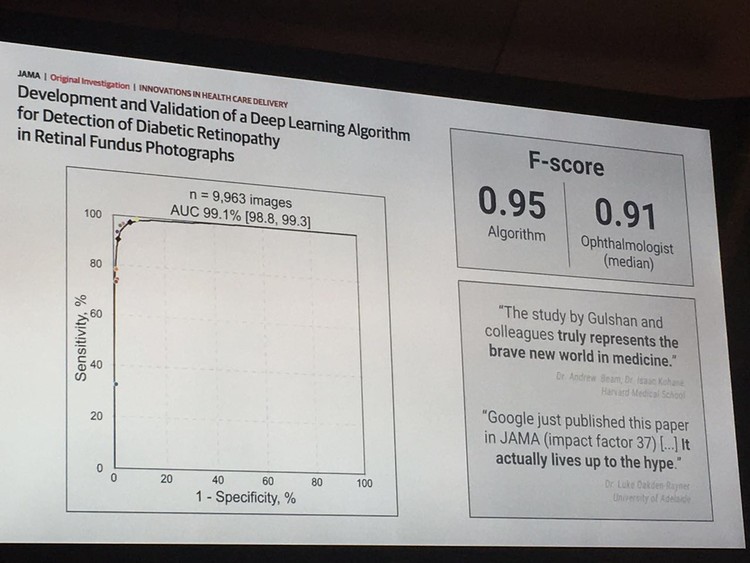
In January and February 2016, Google Research found two different retinal fundus photo libraries for ophthalmology, allowing algorithms and ophthalmologists to compete. The result of this attempt is significant: the algorithm scores higher than the person's score on the sensitivity of the symptom (98.8) and the accuracy of the symptom (99.3) (statistically, this score is called F -score, the ophthalmologist's score is 0.91, and the algorithm gets 0.95).
Shandong Longze Mechanical Equipment Co.,Ltd , https://www.pelletmachinefactory.com