Tumor immunotherapy, such as PD-1 and PD-L1 immunological checkpoint inhibitors, has achieved great success in treating advanced or metastatic lung cancer. However, the current standard treatment for early stage lung cancer is still surgery and chemotherapy. Can tumor immunotherapy be used to treat early stage lung cancer?
Recently, researchers at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in the United States conducted a detailed study of the immune microenvironment of early lung cancer tumors. They found that immune factors that make tumor immunotherapy successful exist in the microenvironment of early lung cancer, which means that immunotherapy is promising for success in early lung cancer patients. The study was published in the journal Cell.
Currently, the common treatment for patients with early stage lung cancer is still surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy. The 5-year survival rates of patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer in IA and IB were 83% and 71%, respectively, while those in stage II were only 50%. This shows that there is still much room for improvement in the treatment of early stage lung cancer. Although immunological checkpoint inhibitors such as PD-1 or PD-L1 antibodies have shown excellent efficacy in the treatment of advanced lung cancer, they have not been used to treat patients with early stage lung cancer. One of the important reasons is that we don't understand the immune status of the microenvironment near the early lung cancer. The success of immunological checkpoint inhibitors depends on whether there are already immune cells that can kill tumors around the tumor, and whether the anti-cancer ability of these immune cells is inhibited by immunological checkpoint proteins such as PD-1 or PD-L1. Therefore, it is important to understand the immune status of the early lung cancer tumor microenvironment.
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine obtained resected tumor tissue, normal lung tissue, and blood samples from patients with early stage lung cancer. They designed a bar code system to label all cells in these three different samples with metal isotopes. Then using time-of-flight mass spectrometry (mass cytometery by time-of-flight) combined with single cell transcriptomics and multiple imaging techniques for lung tumors, the immune status of lung tumors in single cells Perform a detailed analysis on the level.
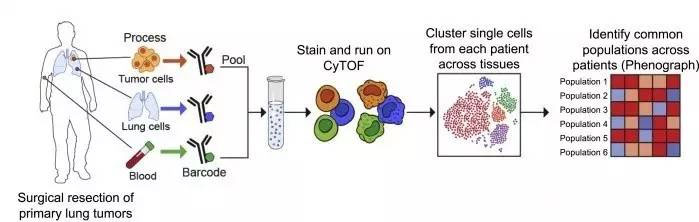
Study on the immune composition of lung cancer samples (Source: Cell)
High-dimensional single-cell profiling of lung cancer tumors at the single cell level indicates that in the early stage of lung cancer, all major immune cell types are clustered around the tumor, the most of which are T lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytic cells. Regulatory T cells have also been enriched around early tumors. The immunological checkpoint proteins PD-1 and PD-L1 have also appeared on the surface of a subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes and macrophages, respectively. These immune features found in advanced lung cancer also exist in early stage lung cancer. This means that PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors are likely to achieve the same effect in early stage lung cancer.
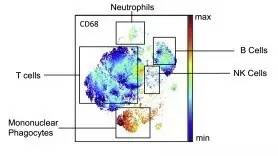
Analysis of micro-environmental immune cell expression in early lung cancer (Source: Cell)
Mackerel
Mackerel,King Mackerel,Jack Mackerel,Saba Mackerel
ZHEJIANG EVERNEW SEAFOOD CO.,LTD , https://www.evernewseafood.com